Whatsup Squad,
The legalization of sports betting has rapidly transformed the sports industry.
And the numbers are staggering.
The Scale of Sports Betting
Since the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in 2018, which allowed each state to regulate sports betting individually, 38 U.S. states, Washington D.C., and Puerto Rico have legalized sports betting in some form.
And it’s easy to see why so many states have joined.
In 2024, the American sports betting industry posted a record $13.7 billion in revenue.
In fact, New Jersey and Illinois surpassed $1 billion in annual sports betting revenue for the first time.
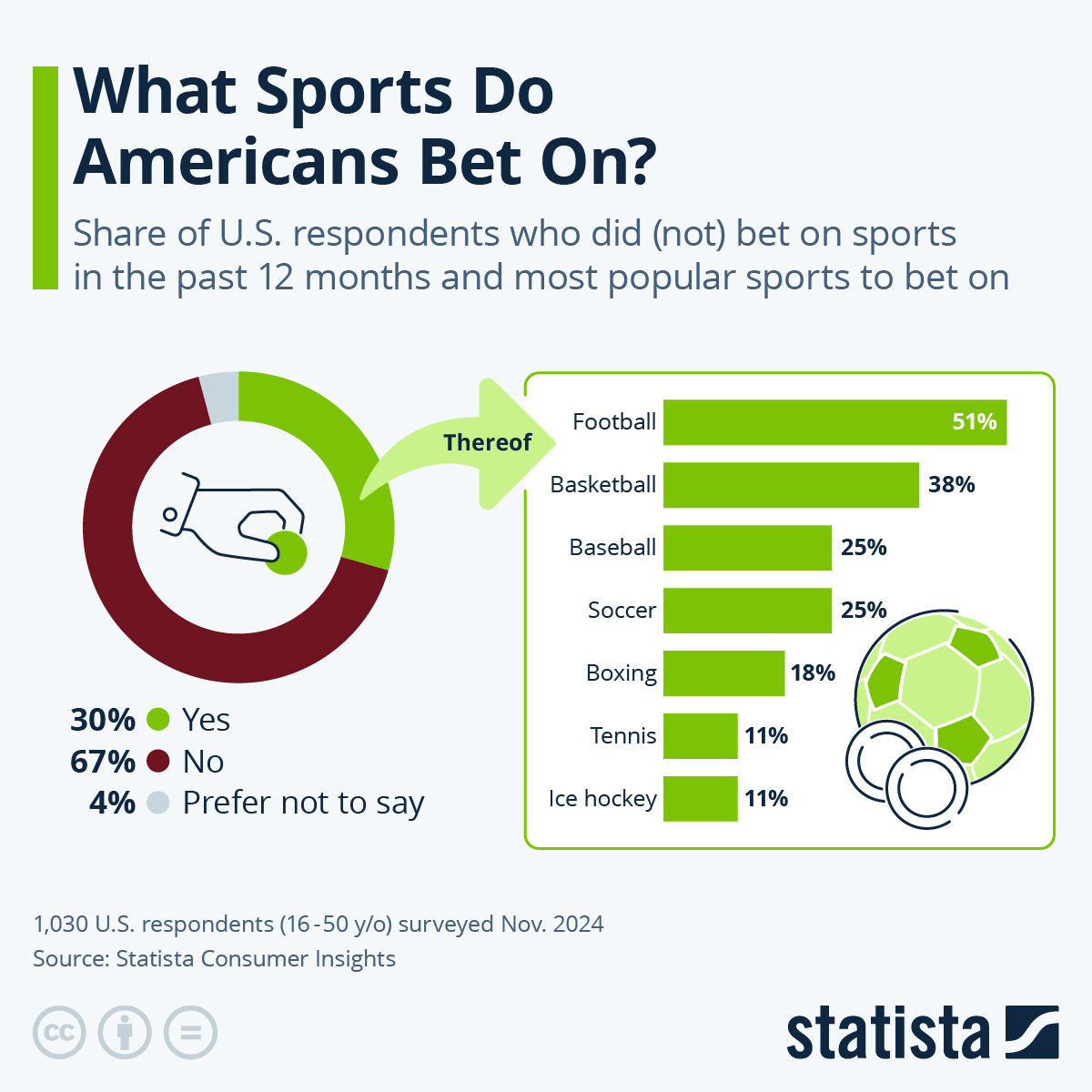
That said, this is just a slice of the action. Americans bet a staggering $148 billion on sports last year, with more than 95% of this happening online.
Football was by far the most popular sport among those betting, with more than half of those active in sports betting putting their money on a football game.
While soccer comes in as the fourth-most popular sport to bet on in America, it is the most popular sport to bet on globally.
Why Bet on Sports?
According to a NerdWallet report, the average American sports bettor spent $3,284 in the past 12 months.
What’s the motivation? Nearly two-thirds of sports bettors (65%) say they participate in sports betting because they want to make extra money.
While it’s possible to profit from sports betting, it is unlikely.
The survey also found that just 40% of sports bettors say they’ve had net gains in the past 12 months, and 14% of sports bettors have gone into debt for gambling.
While this is a developing issue in America, it could be even worse in emerging economies.
Global Impact
The growth of sports betting isn’t exclusive to the United States, as legalization and widespread availability of digital platforms extends into emerging economies.
And as sports betting spreads to countries with less disposable income, the financial risks for bettors will be even greater.
A recent study “Gambling Away Stability: Sports Betting's Impact on Vulnerable Households” found that the introduction of online sports gambling does not displace other spending but instead leads to new overspending and “significantly reduces households’ savings allocations.”
The researchers say access to online sports betting “exacerbates financial difficulties faced by constrained households.”
Using financial data from 230,000 US households, the study linked sports betting to “a large decrease” in deposits to brokerage accounts, accompanied by “decreased credit availability, increased credit card debt, and a higher incidence rate of overdrawing bank accounts.”
While mature markets like the U.S. and the U.K. lead in revenue, regions such as Latin America, India, and Africa offer both untapped potential and unique challenges.
Final Thoughts
While sports betting can boost the economy, there are concerns regarding the potential for financial ruin among users.
The normalization of gambling content is still relatively new, and its long-term effects on professional sports are yet to be fully understood.
For leagues and rights holders, sports betting means more revenue and more engaged fans. For fans, it adds an extra layer of excitement to the viewing experience and the potential to make extra money.
But there’s a darker side: betting on sports is not an investment. It’s a costly gamble.
How these risks and rewards are balanced will ultimately determine the overall health of the sports ecosystem.
If you enjoyed this breakdown, share it with one friend who might like it too.
Until next time ✌🏾